Power outages, whether in the form of blackouts or brownouts, can disrupt our daily lives and create challenges in various aspects and this could be, no doubt, very challenging!
These temporary disruptions in electrical power supply can occur due to a range of factors, from severe weather conditions to infrastructure issues. Understanding the differences between blackouts and brownouts is crucial in comprehending their impact and how to navigate through such situations effectively.
In this informational article, we will explore the distinctions between blackouts and brownouts, shedding light on their causes, characteristics, and potential consequences. We will delve into the dangers posed by these power disruptions, such as safety hazards, disruption of essential services, and others. Moreover, we will provide practical tips on how to manage blackouts and brownouts, including preparation strategies, device management, and safety precautions.
By gaining insights into the nature of blackouts and brownouts, readers will be better equipped to handle these situations, minimize risks, and adapt to temporary power losses.
Here is a guide to understanding power outages so that we are better prepared to navigate them in the future.
First of All, What’s the Difference Between Brownout & Blackout?
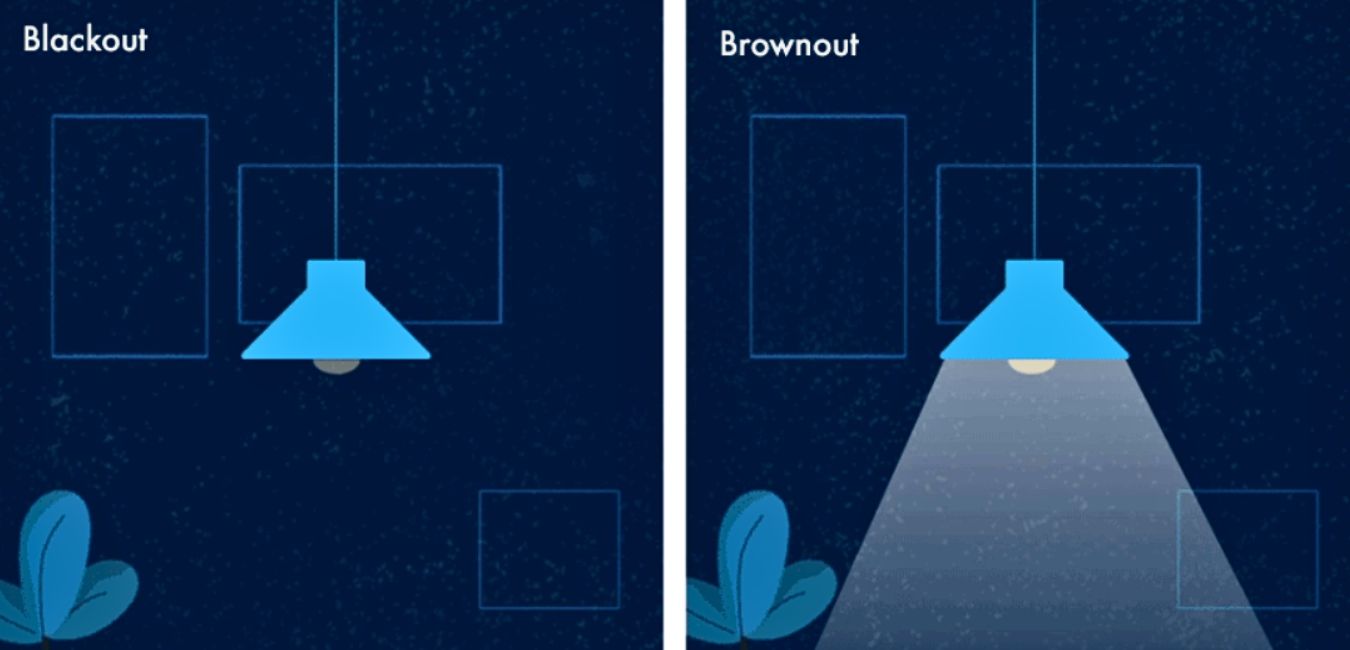
A BROWNOUT refers to a deliberate or unintentional drop in voltage within an electrical power supply system. It is often used as a load reduction measure during emergencies, lasting for minutes or hours. The term “brownout” originated from the dimming effect experienced by lighting when voltage sags.
Energy providers intentionally induce brownouts to prevent a complete system failure, also known as a blackout. During a brownout, some electrical devices may be severely affected, while others may not experience any impact at all.
Sensitive electronic equipment that requires precise voltages might struggle to function properly, and prolonged brownouts can lead to premature wear in non-electronic devices.

On the other hand, a BLACKOUT involves a complete interruption of power in a given service area. Blackouts can be caused by catastrophic equipment failure or severe weather conditions, and they occur without warning.
Unlike brownouts, blackouts are not planned and can last for indeterminate periods. They can pose significant risks, particularly for individuals relying on electricity for medical equipment or life-saving devices.
To cope with peak power demands, utility companies may implement rolling blackouts, which are controlled and preplanned interruptions of service. Rolling blackouts are typically announced in advance and are intended to affect specific service areas without causing excessive strain on any one area.
What’s the Cause of Brownouts and Blackouts?
BROWNOUTS are often intentionally induced by energy providers as a proactive measure to prevent complete system failures, or they can occur as a result of disturbances in the electrical grid.
The intentional reduction in voltage during brownouts is a way to alleviate excessive demand and prevent the overloading of the system. On the other hand, disturbances in the electrical grid, such as equipment malfunctions or sudden power surges, can also lead to voltage drops and result in unintentional brownouts.
BLACKOUTS, on the other hand, are typically caused by more severe and uncontrollable events. Extreme weather conditions, such as storms, hurricanes, or heavy snowfall, can damage power lines, transformers, and other infrastructure, leading to widespread blackouts.
Equipment failures, such as a major malfunction at a power plant or a critical component of the electrical grid, can also trigger blackouts. In some cases, human errors, such as mistakes in system operations or maintenance, can contribute to blackouts as well.
To minimize the occurrence of brownouts and blackouts, utility companies invest in infrastructure maintenance and upgrades, ensuring the stability and reliability of the electrical grid. Advanced monitoring systems are employed to detect potential issues and allow for timely interventions.
Additionally, promoting energy conservation and spreading awareness about responsible energy usage can help mitigate the strain on the power grid, reducing the likelihood of power disruptions.
Things You Should Do in Case of a Brownout or Blackout!
Here are some important steps to take in case of a brownout or blackout:
- Check Your Circuit Breaker: If you notice a sudden loss of power, check your circuit breaker to ensure that it hasn’t tripped. Resetting the breaker may resolve the issue if it is a localized problem.
- Preserve Food and Perishables: Keep refrigerator and freezer doors closed as much as possible during the outage to maintain the cold temperature. This will help preserve food and prevent spoilage.
- Use Alternative Lighting: Keep flashlights, battery-operated lanterns, and candles in an easily accessible location. Avoid using open flames for lighting to reduce the risk of fire hazards.
- Unplug Electronics: Unplug sensitive electronic devices, such as computers, TVs, and gaming consoles, to protect them from power surges when the electricity is restored.
- Conserve Energy: Reduce energy consumption by turning off unnecessary lights and appliances. Unplug non-essential devices to prevent power drain once the electricity comes back on.
- Stay Informed: Use a battery-powered or hand-cranked radio to stay updated on the latest information about the outage. Local authorities and utility companies often provide updates on the restoration process.
- Keep Emergency Supplies Handy: Have a well-stocked emergency kit that includes essentials such as bottled water, non-perishable food, a first aid kit, extra batteries, and a portable phone charger.
- Stay Safe: Use caution when using alternative heating sources or power generators. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and ensure proper ventilation to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
Rolling Blackouts: What Are They?
Rolling blackouts are a common phenomenon in areas with high energy consumption. They occur when there is an insufficient supply of electricity to meet the demands of consumers, leading to power outages for short periods. Unlike regular blackouts that can last for hours or even days, rolling blackouts happen intermittently and rotate through different neighbourhoods.

These outages usually occur during peak usage times such as hot summer afternoons when air conditioners are running at full blast. To prevent overloading the grid, utility companies will implement rolling blackouts by cutting off power to specific areas for approximately 1-2 hours before restoring it and moving on to another location.
Although they might be frustrating if you’re hit by one, rolling blackouts help maintain stability within our electrical systems and prevent more significant disruptions from occurring down the line.
If There’s a Blackout or Brownout, How Can EcoFlow DELTA Portable Power Stations Help?
When faced with a blackout or brownout, many households and businesses are left scrambling for alternative power sources. This is where the EcoFlow DELTA Portable Power Stations come in handy.
These devices provide an immediate backup source of power during outages, allowing you to keep your essential appliances running seamlessly until the main power supply is restored.
Versatile Power for Smartphones to Electric Stoves
The EcoFlow DELTA can support up to 13 devices at once, from smartphones and laptops to refrigerators and electric stoves.
Compact & Portable Power Anywhere, Anytime!
Another great feature of the EcoFlow DELTA is its compact size and portability. Weighing only 30 pounds, this device can be easily moved around so that you have access to reliable power wherever you go.
Investing in an EcoFlow DELTA Portable Power Station ensures uninterrupted access to electricity when needed most while avoiding potential damage caused by voltage fluctuations during blackouts or brownouts.

Unmatched Battery Life
What sets EcoFlow DELTA apart from other portable generators is its impressive battery life – it can last up to 20 hours on a single charge depending on usage. It also has multiple charging options including solar panels which makes it ideal for outdoor use.
Solar Panels Can be Attached as Well!
The DELTA models are designed to be compatible with solar panels. With solar compatibility, charging is easier, especially in situations where the duration of a blackout is unknown. Different DELTA models accommodate different sizes and power requirements with solar inputs ranging from 300W to 1600W.
In addition to using renewable energy sources to generate power, solar power can reduce reliance on the electricity grid, and make power available during extended outages or periods of limited access to traditional power sources.
What’s a Power Surge?
A power surge is a sudden and unexpected increase in the electrical current flowing through your home or office’s wiring system. This sudden spike in electricity can cause significant damage to electronic devices, appliances, and equipment that are connected to the power supply.
Power surges can be caused by several factors, including lightning strikes, faulty wiring systems, or problems with the local power grid. They can also occur when large appliances such as refrigerators or air conditioners turn on and off repeatedly.

Brownout Vs Power Surge
Brownouts and power surges are two common electrical problems that can cause damage to electronic devices. A brownout is a temporary drop in voltage that causes lights to dim or flicker, while a power surge is an increase in voltage that can occur during lightning strikes or when the power comes back on after an outage.
A brownout occurs when there isn’t enough electricity flowing through the lines to meet demand. This results in lower voltage levels which can lead to equipment malfunction or failure over time. On the other hand, a power surge happens when too much electricity flows into your home all at once – like from a lightning strike – which puts excessive strain on your electronics causing them to burn out.
To protect against both of these electrical issues, it’s important to invest in high-quality surge protectors for all of your major electronic devices including computers, printers and refrigerators among others!
Brownout Vs Voltage Sag
When it comes to power disruptions, brownouts and voltage sags may seem similar, but they have distinct differences. A voltage sag is a brief drop in the power supply that lasts for less than a second while a brownout is a sustained reduction of the electrical grid’s voltage.
Voltage sags often occur due to momentary faults such as lightning strikes or when high-power equipment is switched on suddenly. They can cause damage to sensitive electronics if not protected by surge protectors or uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). On the other hand, brownouts typically happen during peak electricity usage hours when demand outstrips supply.
Therefore, both are serious issues that homeowners and businesses need to take seriously by investing in proper protection measures like UPS systems and surge protectors.
Brownouts and Blackouts: Which Devices Could Be at Risk?
When it comes to brownouts or blackouts, almost all electronic devices could be at risk. You never know which one would get affected. However, some major devices that could most probably be at risk are:

- Televisions
- Computers
- Refrigerators
- Washers/Dryers
- Toasters
- Telephones on landlines
- Microwaves and Ovens
- Clocks
- Lamps
- Anything with a power cord
- Power strips
- Hair dryers, straighteners etc.
- Coffee machines
Whom Should You Call When a Brownout or Blackout Occurs?
In the event that a blackout or brownout occurs, it is recommended to contact your local power utility company or electricity provider. They are responsible for the distribution and maintenance of the power grid in your area.
By contacting them, you can report the blackout and get updates on the status of power restoration efforts. The contact information for your utility company can usually be found on your electricity bill or by searching online for the appropriate utility company in your region.
During a blackout, it is important to maintain communication with your local electricity grid. Consider enrolling in the electricity grid’s alert system, if available, to receive email or text notifications during such occurrences.
Conversely, if the local utility confirms that everything is functioning normally and the issue seems to be limited to your own property, it may be a brownout caused by internal electrical problems. In such situations, it is advisable to contact an emergency electrician for assistance.
Dangers of Blackout and Things You Must Unplug When There’s a Blackout!
Blackouts can pose several dangers and risks. Here are some common dangers associated with blackouts:

- Safety Hazards: Blackouts can lead to a lack of lighting, making it difficult to navigate safely in both indoor and outdoor environments. This increases the risk of accidents, falls, and injuries.
- Disruption of Essential Services: Blackouts can disrupt essential services such as emergency response systems, hospitals, communication networks, and water supply. This can hinder rescue efforts, medical procedures, and communication during emergencies.
- Extreme Temperatures: In certain regions or seasons, blackouts can coincide with extreme temperatures, such as heat waves or cold snaps. Without access to heating or cooling systems, individuals may be exposed to dangerous temperature conditions, increasing the risk of heatstroke, hypothermia, or other weather-related health issues.
- Security Risks: Blackouts can create an environment conducive to criminal activities, including burglary, looting, and vandalism. The lack of security systems and street lighting can make homes and businesses more vulnerable.
- Disruption of Transportation: Traffic lights and transportation systems heavily rely on electricity. A blackout can cause traffic congestion, accidents, and delays due to non-functional traffic signals and disruptions in public transportation services.
NOTE: It is important to stay prepared for blackouts by having emergency supplies, alternative lighting sources, and a contingency plan in place to mitigate these risks and ensure personal safety.
Following are the devices that you must unplug whenever there’s a brownout or blackout.
The following devices should be unplugged or turned off during a blackout or power outage to prevent damage if power is restored:
- Computers and Sensitive Electronics: You should unplug your computer, laptop, printer, router, modem, gaming console, and other sensitive electronic devices. Because circuitry might be damaged by power surges during blackouts.
Televisions and Entertainment Systems: Avoid damage to televisions, DVD players, audio equipment, and other entertainment devices by unplugging them too. - Kitchen Appliances: Make sure the major kitchen appliances are unplugged, such as the refrigerator, freezer, oven, microwave, and dishwasher. To prevent food spoilage, keep refrigerator and freezer doors closed.
Air Conditioners and Heaters: Disconnect and unplug air conditioners, space heaters, and other HVAC systems to avoid power surges after the electricity is restored. - Washing Machines and Dryers: Make sure washers and dryers are unplugged before turning the power back on to prevent them from starting unexpectedly.
- Home Office Equipment: It is best to unplug photocopiers, scanners, fax machines, and other office equipment also, in order to prevent power surges from damaging them.
- Chargers and Power Adapters: Disconnect chargers and adapters for portable devices such as mobile phones, tablets, and laptops. Leaving some chargers plugged in may draw power even when they are not charging.
There are certain devices that require a continuous power supply, like alarm systems, medical equipment, or essential home safety equipment. Consult a professional for specific advice about these devices or refer to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Some Tips That Can Help You Manage Blackouts & Brownouts
Certainly! Here are some tips to help you manage blackouts and brownouts:

- Preparing an emergency kit is essential: Include items like flashlights, batteries, candles, matches, a hand-crank radio, a first aid kit, and non-perishable food items in your emergency kit. Blackouts or brownouts can be more manageable with these supplies readily available.
- Unplug Sensitive Electronics: As mentioned earlier, unplug or turn off sensitive electronics to protect them from power surges when the electricity is restored. This can help prevent damage to devices such as computers, TVs, and home theatre systems.
- Report the Outage: Contact your local power utility company to report the outage and provide any necessary information. This can help them track and prioritize restoration efforts.
- Have a Backup Power Source: Consider investing in a backup power source, such as a portable generator or a battery backup system, to provide temporary power during outages. This can help keep essential devices running, such as medical equipment or necessary appliances. Make sure you make generators safe for the electronics.
- Install power strips: Power strips are useful for a variety of reasons. In addition to protecting your devices from power surges, they also allow you to plug in multiple devices simultaneously and reduce cord clutter.
- Get a Whole-Home Surge Protector Installed: The installation of a whole-home surge protector will require a licensed electrician, but the benefit is that it will keep your devices safe. It just takes a couple of hours to install a whole-house surge protector on your service panel. During brownouts or blackouts, this is useful if you are not home.
Remember, safety should always be a priority during blackouts and brownouts. If you have any concerns or encounter potentially hazardous situations, contact your local emergency services for assistance.
Brownout Vs Blackout – FAQs
Our Verdict
In conclusion, blackouts and brownouts both represent disruptions in electrical power supply, albeit with varying degrees of severity. Blackouts, characterized by a complete loss of power, can result in widespread inconvenience and potential safety risks. On the other hand, brownouts involve a reduction in voltage and can cause equipment damage and operational issues.
We hope we’ve been helpful to our readers through this guide on understanding blackouts and brownouts!