The use of generators has simplified the process of converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. The wind, water in motion, and engines are just a few examples of the many sources that can provide this mechanical energy. However, how did this potent element come to be? Who developed the first generator and how did it function? The highlights of a generator’s development in chronological order, from its inception to the present-day model, are discussed below.
At the very beginning – the 1700s
The usage of steam engines began in the 18th century, setting the stage for the eventual development of generators. James Watt observed a significant energy loss during the running of the Newcomen 1712 steam engine.
When starting, this engine needed a lot of heat energy to warm up the cylinders, and it also needed a lot of water to keep cool while running. In 1781, he created the Watt Steam Engine, which included more effective energy-conserving systems.
The improvement of engines, which included rotating motions in the functioning mechanism, began with Watt’s invention.
Later, this would lead to the construction of generators, which eventually created the watt—named for him—unit of power.
The 1800s saw the advent of electricity
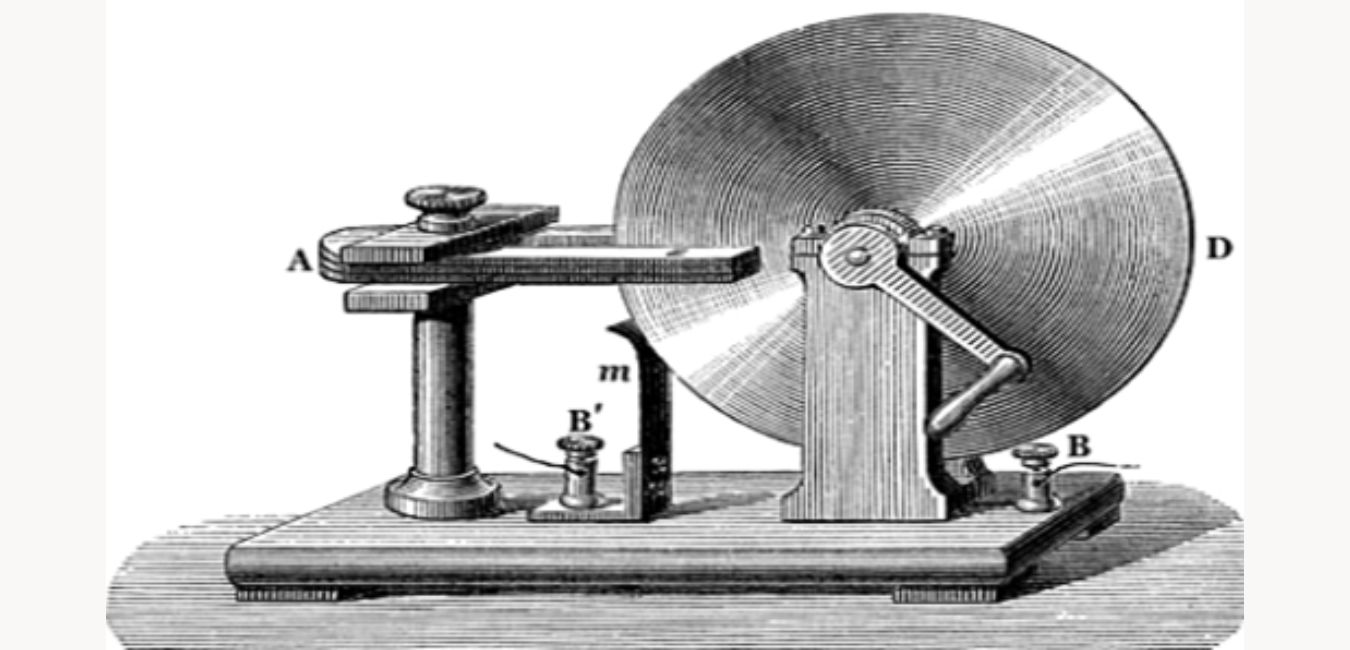
Early in the 1800s, Michael Faraday made a vital contribution to the development of electricity. He created a magnetic generator with a Faraday disc in 1831. It involved rotating a copper disc between two magnets with their poles perpendicular to the copper disc. The generator generated comparatively
Although the generator produced little voltage, it produced a lot of currents. The creation of dynamos, the first of which was constructed in 1832, used faraday’s magnetic principle. A key innovation that led to the introduction of electricity for use in industries was the development of the dynamo.
From Faraday’s premise, numerous inventions were made in the middle of the 1800s. In 1860, German scientists like Werner Von Siemens promoted two technologies that featured DC and AC generators. Over time, improvements were made, and Thomas Edison launched the electric lighting system in the late 1870s using DC generators. This method assisted in supplying residences and the light industry with electricity. Several industries had already adopted the technique by the early 1880s, and it would eventually become commercial.
Several industries installed the systems in the early 1880s before the system went commercial.
By significantly enhancing the already-existing AC generator, Nikola Tesla made substantial contributions to the advancement of generators in 1887. Tesla created Polyphase AC, which integrated several outputs into a single phase in place of conventional individually revolving poles. As a result of the invention’s ability to create vast amounts of power, it was used in large corporations.
The 1900s: Expansion Generators
By the start of the 20th century, a number of businesses producing generators had already been established following these key discoveries and advancements. Since the two use a similar mechanism, the creation of the motor also included the production of generators. Steam turbines, water turbines, and other sources provided mechanical energy for the generators.
The generators’ mechanical energy came from a variety of sources, including steam turbines, water turbines, and gas turbines. These turbines may rotate alongside the generator poles, producing a current as a result.
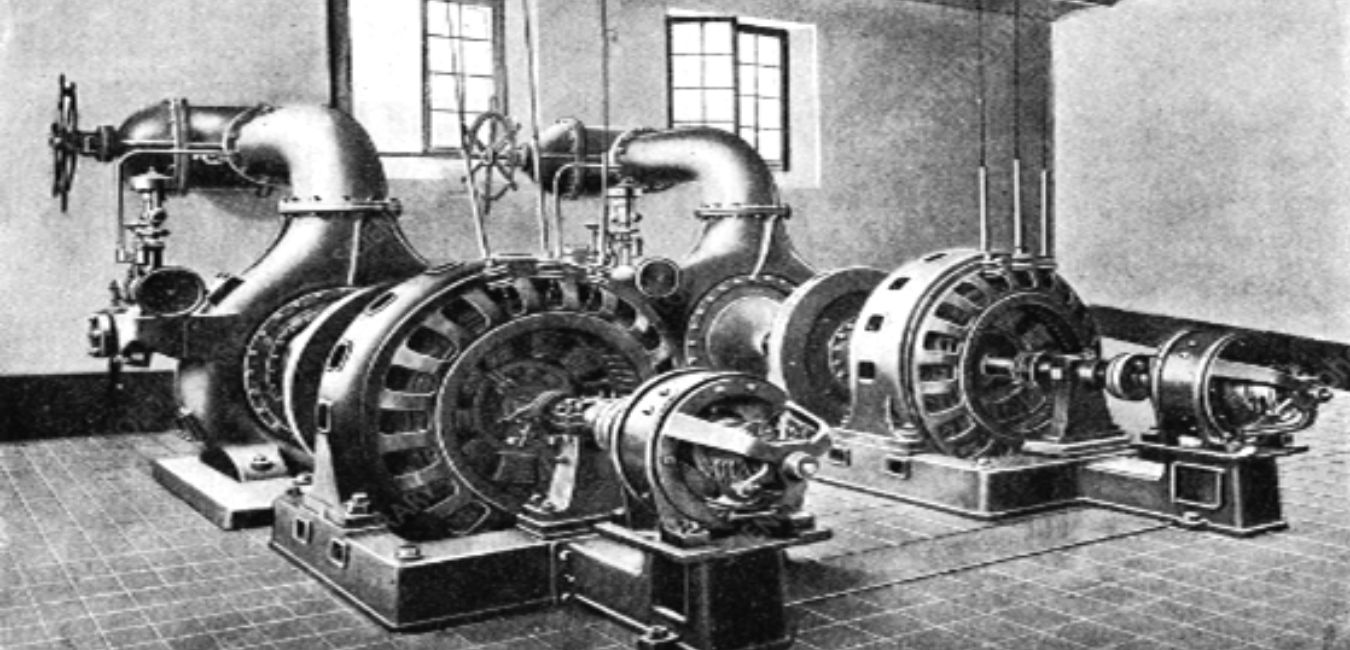
Back then, companies that produced generators could design the entire unit and then install it for a specific enterprise. In addition, power generation facilities were built to supply electricity to various targets. As a result, grid systems with localized electrical supplies were developed.
Portable generators from the 2000s are modern
The present design involves combining an engine and generator into a single unit. The so-called engine generator, which can be relocated to multiple locations, has grown in importance for supplying power. The device typically includes an engine, a fuel tank, a voltage regulator, and a battery.
An engine, a fuel tank, a voltage regulator, and a speed regulator typically make up the unit. Particularly for big portable engine generators, it also contains a starting mechanism that comprises a battery and a starter. Small portable generators, however, can be manually started by drawing a lash. Since the majority of current equipment uses AC current, portable generators often provide this kind of electricity.
Engine generators come in both single-phase and three-phase varieties. However, only a small number of three-phase portable generators are available, and the majority are only accessible in single-phase variants. Depending on their size, they have different power ratings.
While large generators use fuels like diesel and natural gas, small, portable generators typically run on gasoline. Additionally, portable generators using two fuels are available.
Currently, generators mostly serve to supplement the nation’s electrical grid. However, they typically provide enough power to meet a variety of needs, including domestic lights and small-scale commercial usage. Additionally, they are mostly utilized in regions where the grid system has not yet been established. Lighting roving carnivals with trailer-mounted generators is another application.
Compared to earlier generations, modern generators are a lot quieter. This is particularly true with generators that use inverter technology. These are common options for camping and travel trailers in addition to homes and construction.
History of Generators – FAQs
How often do generators need to be serviced?
A generator should, at the very least, have its oil and filters changed once a year while being serviced by a professional.